Visio Professional 2019 Visio Standard 2019 Visio 2013 Visio Professional 2016 Visio Standard 2016 Visio 2010 Visio 2007 Visio Online Plan 2 Visio Premium 2010 Visio Professional 2013 Visio Standard 2007 Visio Standard 2010You can use Visio to build Unified Modeling Language (UML) use case diagrams. Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standard way to draw software models.Defining the system boundary determines what is considered external or internal to the system.An actor represents a role played by an outside object.
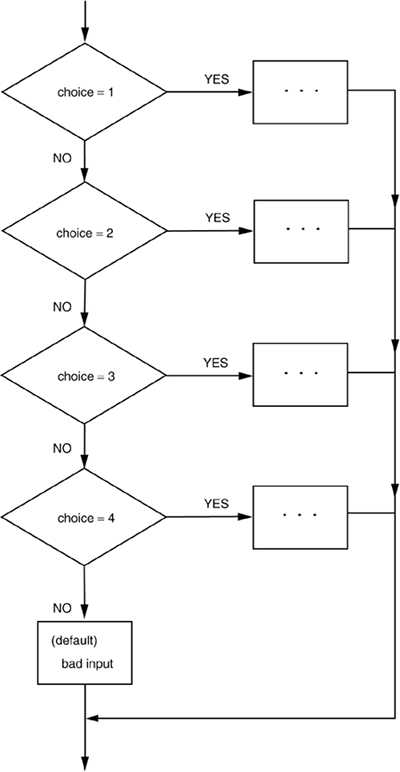
Flowcharts For Switch Statements
One object may play several roles and, therefore, is represented by several actors.A communicates relationship illustrates the participation of the actor in the use case.A use case is a set of events that occurs when an actor uses a system to complete a process. Normally, a use case is a relatively large process, not an individual step or transaction.On the File tab, point to New, and then open a blank diagram.Click More Shapes Software and Database Software UML Use Case.To indicate a subsystem in a use case diagram.Drag a Subsystem shape onto the drawing page.
The subsystem can represent your entire system or a major component.Double-click the Subsystem shape, and then type a new name for the for it, or press the DELETE key to delete the existing name. Click outside the shape on the drawing page.To resize the subsystem, select the shape, and then drag a selection handle.Drag from the Use Case stencil and place them inside the subsystem boundary, and then drag to the outside of the subsystem boundary.Use connector shapes to indicate relationships between use cases and actors. Note: If the tree view is not visible, on the UML tab, in the Show/Hide group, select Model Explorer.To indicate a in a use case diagram.Drag a System Boundary shape onto the drawing page.Double-click the System Boundary shape, and then type a new name for the system or press the DELETE key to delete the existing name. Click outside the shape on the drawing page.To resize the system boundary, select the shape, and then drag a selection handle.Drag from the Use Case stencil and place them inside the system boundary, and then drag to the outside of the system boundary.Use to indicate relationships between use cases and actors.To indicate a relationship between an actor and a use case.In a use case diagram, drag a Communicates shape onto the drawing page.Glue one endpointof the Communicates shape to a connection pointon an Actor shape. Glue the other endpoint to a connection point on a Use Case shape.If you want to add an arrow to indicate the flow of information, do the following:.Double-click the Communicates shape, then, under Association, click the end you want to edit, and then click Properties.In the Association End category, check IsNavigable, click OK, then click OK again.Right-click the Communicates shape and click Shape Display Options.
Under End options, select End navigability, and then click OK.Use Uses and Extends shapes to indicate the relationships between use cases.To indicate a uses relationship between two use cases.In a use case diagram, drag a Uses relationship shape onto the drawing page.Glue the Uses endpoint without an arrowhead to a connection pointon the Use Case shape that uses the behavior of the other use case.Glue the Uses endpoint (with an arrowhead) to a connection point on the use case being used.Double-click the Uses shape to open the UML Generalization Properties dialog box. Add property values, and then click OK.To indicate an extends relationship between two use cases.In a use case diagram, drag an Extends shape onto the drawing page.Glue the Extends endpointwithout an arrowhead to a connection pointon the use case providing the extension.Glue the Extends endpoint with an arrowhead to a connection point on the base use case.Double-click the Extends shape to open the UML Generalization Properties dialog box. Add the property values, and then click OK.Double-click any shape (except the System Boundary shape) to open its UML Properties dialog box where you can add a name, attributes, operations, and other property values.Save the diagram. Note: If the tree view is not visible, on the UML menu, point to View, and then click Model Explorer.To indicate a system boundary in a use case diagram.Drag a System Boundary shape onto the drawing page.Double-click the System Boundary shape, and then type a new name for the system or press the DELETE key to delete the existing name. Click outside the shape on the drawing page.To resize the system boundary, select the shape, and then drag a selection handle.Drag from the Use Case stencil and place them inside the system boundary, and then drag to the outside of the system boundary.Use to indicate relationships between use cases and actors.To indicate a relationship between an actor and a use case.In a use case diagram, drag a Communicates shape onto the drawing page.Glue one endpointof the Communicates shape to a connection pointon an Actor shape.
Switch Case In C Programming Examples Pdf
Glue the other endpoint to a connection point on a Use Case shape.If you want to add an arrow to indicate the flow of information, do the following:.Double-click the Communicates shape, then, under Association, click the end you want to edit, and then click Properties.In the Association End category, check IsNavigable, click OK, then click OK again.Right-click the Communicates shape and click Shape Display Options. Under End options, select End navigability, and then click OK.Use Uses and Extends shapes to indicate the relationships between use cases.To indicate a uses relationship between two use cases.In a use case diagram, drag a Uses relationship shape onto the drawing page.Glue the Uses endpoint without an arrowhead to a connection pointon the Use Case shape that uses the behavior of the other use case.Glue the Uses endpoint (with an arrowhead) to a connection point on the use case being used.Double-click the Uses shape to open the UML Generalization Properties dialog box. Add property values, and then click OK.To indicate an extends relationship between two use cases.In a use case diagram, drag an Extends shape onto the drawing page.Glue the Extends endpointwithout an arrowhead to a connection pointon the use case providing the extension.Glue the Extends endpoint with an arrowhead to a connection point on the base use case.Double-click the Extends shape to open the UML Generalization Properties dialog box. Add the property values, and then click OK.Double-click any shape (except the System Boundary shape) to open its UML Properties dialog box where you can add a name, attributes, operations, and other property values.Save the diagram.